The ABO/Rh simulated blood typing worksheet provides a hands-on and engaging approach to understanding the principles of blood typing and Rh factor determination. This comprehensive guide explores the significance of blood typing, explains the simulated blood typing process, and discusses its applications in various settings.
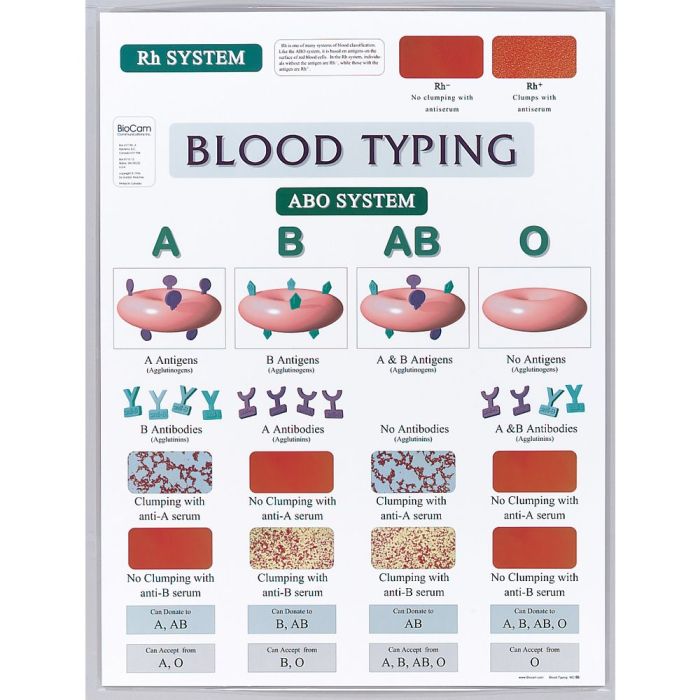
Blood typing is a fundamental aspect of healthcare, as it helps determine blood compatibility for transfusions and organ transplantation. The ABO/Rh system is the most widely used blood typing system, classifying blood into four main types (A, B, AB, and O) based on the presence or absence of specific antigens on red blood cells.
The Rh factor is another important blood group antigen that can be either positive or negative.
1. Introduction to ABO/Rh Simulated Blood Typing
Blood typing is a crucial procedure in healthcare, determining an individual’s blood type to ensure safe blood transfusions and prevent adverse reactions. The ABO blood typing system and Rh factor are fundamental concepts in blood typing. Simulated blood typing worksheets provide a valuable tool for learning and practicing these principles.
2. Materials and Methods
Materials:, Abo/rh simulated blood typing worksheet
- Simulated blood typing worksheet
- Blood typing antisera (Anti-A, Anti-B, Anti-Rh)
- Microscope slides or microplates
- Pipettes or droppers
Procedure:
- Place a drop of simulated blood on the designated area of the worksheet.
- Add a drop of each antiserum (Anti-A, Anti-B, Anti-Rh) to the respective wells or circles.
- Mix the blood and antiserum gently.
- Observe the reactions under a microscope or with the naked eye.
3. Blood Typing Reactions
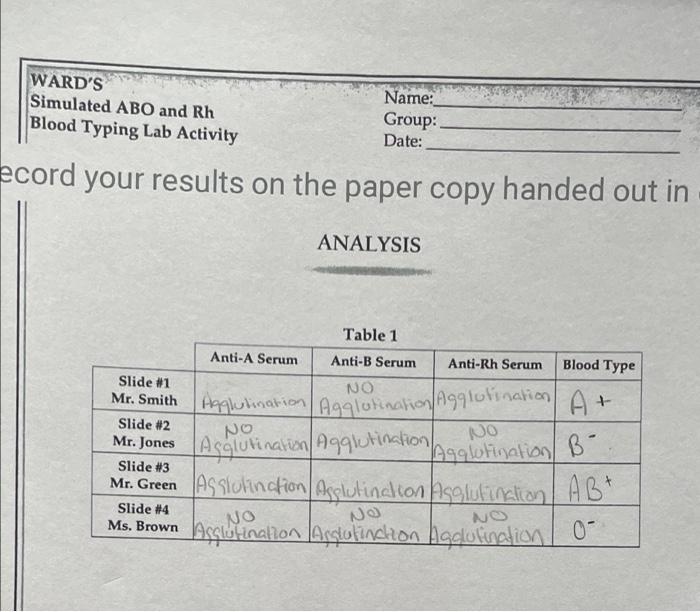
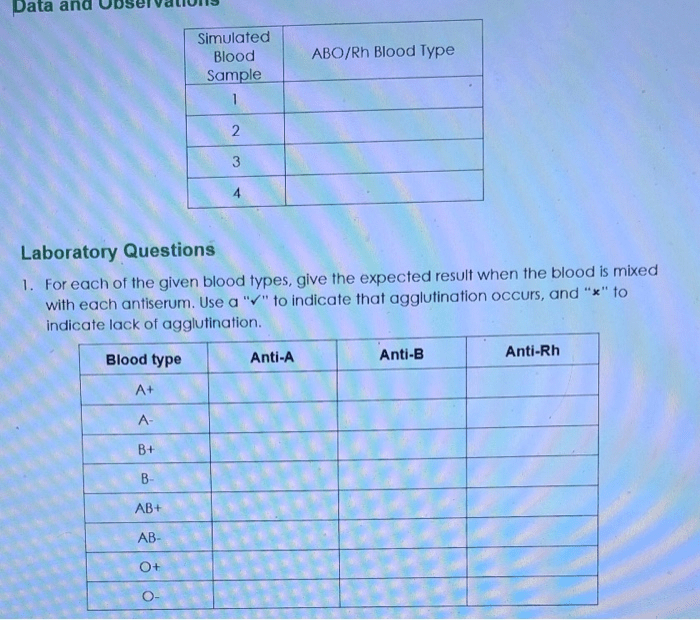
| Blood Type | Anti-A Serum | Anti-B Serum | Anti-Rh Serum | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A+ | Agglutination | No agglutination | Agglutination | Anti-A positive, Anti-B negative, Anti-Rh positive |
| A- | Agglutination | No agglutination | No agglutination | Anti-A positive, Anti-B negative, Anti-Rh negative |
| B+ | No agglutination | Agglutination | Agglutination | Anti-A negative, Anti-B positive, Anti-Rh positive |
| B- | No agglutination | Agglutination | No agglutination | Anti-A negative, Anti-B positive, Anti-Rh negative |
| AB+ | Agglutination | Agglutination | Agglutination | Anti-A positive, Anti-B positive, Anti-Rh positive |
| AB- | Agglutination | Agglutination | No agglutination | Anti-A positive, Anti-B positive, Anti-Rh negative |
| O+ | No agglutination | No agglutination | Agglutination | Anti-A negative, Anti-B negative, Anti-Rh positive |
| O- | No agglutination | No agglutination | No agglutination | Anti-A negative, Anti-B negative, Anti-Rh negative |
Agglutination indicates a positive reaction, while no agglutination indicates a negative reaction.
4. Troubleshooting
- Insufficient mixing: Ensure thorough mixing of blood and antisera.
- Incorrect antisera: Verify the antisera labels and their reactivity.
- Outdated reagents: Replace expired antisera or simulated blood.
- Contamination: Use sterile techniques and avoid cross-contamination between samples.
- Reading errors: Examine the reactions carefully under a microscope or with adequate lighting.
5. Applications of Simulated Blood Typing: Abo/rh Simulated Blood Typing Worksheet
- Educational purposes:Reinforce understanding of ABO blood typing and Rh factor principles.
- Blood transfusion practice:Simulate blood typing procedures to enhance proficiency.
- Research:Study blood group antigens and antibodies, as well as investigate new blood typing methods.
- Quality control:Verify the accuracy and reliability of blood typing reagents and procedures.
Common Queries
What is the purpose of blood typing?
Blood typing is performed to determine the type of blood a person has, which is essential for safe blood transfusions and organ transplantation. It helps ensure that the recipient’s immune system does not attack the transfused blood or organ.
What are the different blood types?
The ABO blood group system classifies blood into four main types: A, B, AB, and O. Each blood type has a specific combination of antigens on the surface of red blood cells.
What is the Rh factor?
The Rh factor is another important blood group antigen. People with a positive Rh factor have the Rh antigen on their red blood cells, while those with a negative Rh factor do not.