Welcome to the definitive guide to student exploration cladograms answer key, your gateway to understanding the intricate tapestry of evolutionary relationships. This comprehensive resource delves into the fundamentals of cladograms, empowering you to construct, analyze, and interpret these essential tools for deciphering the history of life on Earth.
As we embark on this scientific expedition, we will unravel the mysteries of cladograms, uncovering their purpose, key features, and the diverse applications that have revolutionized our understanding of the natural world.
Student Exploration: Cladograms: Student Exploration Cladograms Answer Key
A cladogram is a diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships between different groups of organisms. It is a branching diagram that shows the common ancestors and descendants of different groups, and the order in which they evolved.
The key features of a cladogram are:
- Nodes: Nodes represent common ancestors.
- Branches: Branches represent the lineages that descend from the nodes.
- Terminal taxa: Terminal taxa are the groups of organisms that are at the tips of the branches.
- Character states: Character states are the traits that are used to determine the relationships between the groups of organisms.
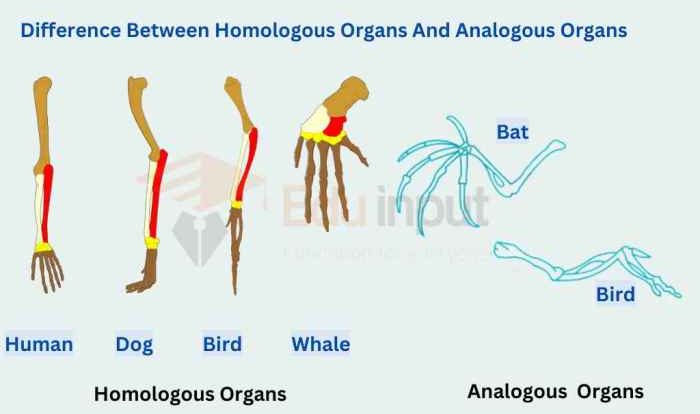
Here is an example of a simple cladogram:

This cladogram shows the evolutionary relationships between four groups of animals: fish, amphibians, reptiles, and mammals. The common ancestor of all four groups is at the base of the cladogram. The branches represent the lineages that descend from this common ancestor. The terminal taxa are the four groups of animals at the tips of the branches. The character states that were used to determine the relationships between the groups of animals are listed on the left side of the cladogram.
Cladogram Construction
Cladograms can be constructed using a variety of different methods. The most common method is called the parsimony method. The parsimony method finds the tree that requires the fewest evolutionary changes to explain the data.
The steps involved in constructing a cladogram using the parsimony method are:
- Gather data on the character states of the groups of organisms that you are interested in.
- Create a matrix of the character states.
- Use a computer program to find the tree that requires the fewest evolutionary changes to explain the data.
There are a variety of different types of data that can be used to construct cladograms. The most common types of data are morphological data and molecular data.
- Morphological data is data on the physical characteristics of organisms.
- Molecular data is data on the DNA or RNA of organisms.
Cladogram Analysis

Cladograms can be analyzed using a variety of different methods. The most common methods are:
- Outgroup comparison: Outgroup comparison is a method of rooting a cladogram. Rooting a cladogram means determining which group of organisms is the outgroup. The outgroup is the group of organisms that is most closely related to the ingroup, but is not part of the ingroup.
- Character weighting: Character weighting is a method of assigning different weights to different character states. This can be done to reflect the relative importance of different character states.
- Bootstrapping: Bootstrapping is a method of assessing the support for different branches on a cladogram. Bootstrapping involves resampling the data and constructing a new cladogram for each resampled data set.
Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages. The best method for analyzing a cladogram will depend on the specific data set and the questions that you are interested in answering.
Cladogram Applications
Cladograms have a wide variety of applications in the fields of biology and evolution. Some of the most common applications include:
- Classifying organisms: Cladograms can be used to classify organisms into different groups. This can help to organize our understanding of the diversity of life on Earth.
- Understanding evolutionary relationships: Cladograms can be used to understand the evolutionary relationships between different groups of organisms. This can help us to learn about the history of life on Earth and how different groups of organisms have evolved over time.
- Making predictions: Cladograms can be used to make predictions about the characteristics of organisms that have not yet been discovered. This can help us to understand the potential diversity of life on Earth and to identify new species.
Cladograms are a powerful tool for understanding the diversity of life on Earth and the history of evolution. They have a wide variety of applications in the fields of biology and evolution, and they continue to be an important tool for scientists.
Essential FAQs
What is the primary purpose of a cladogram?
A cladogram is a diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships among different groups of organisms, providing a visual representation of their shared ancestry.
What are the key features of a cladogram?
Cladograms are characterized by their branching structure, where each branch represents a lineage of organisms that share a common ancestor. They also include nodes, which represent the points where lineages diverge from one another.
How do I interpret a cladogram?
To interpret a cladogram, follow the branches from the root (the common ancestor) to the tips (the extant species). The length of the branches can indicate the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred along that lineage.