Ap biology laboratory 1 diffusion and osmosis – AP Biology Laboratory 1: Diffusion and Osmosis offers a comprehensive exploration into the fundamental processes of diffusion and osmosis, shedding light on their critical roles in biological systems. This engaging laboratory experience delves into the concepts of passive transport, exploring the factors that influence the movement of molecules across semipermeable membranes.
Through hands-on experimentation and data analysis, students gain a deep understanding of these essential mechanisms, their applications in biological systems, and their relevance to homeostasis, medical advancements, and industrial processes.
Diffusion and Osmosis Concepts

Diffusion is the net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane.Diffusion and osmosis are essential processes in biological systems.
They allow for the exchange of nutrients, waste products, and other molecules between cells and their environment. The factors that affect the rate of diffusion and osmosis include the concentration gradient, the surface area of the membrane, the thickness of the membrane, and the temperature.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Diffusion and Osmosis
*
-*Concentration Gradient
The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion and osmosis.
-
-*Surface Area of the Membrane
The larger the surface area of the membrane, the faster the rate of diffusion and osmosis.
-*Thickness of the Membrane
The thicker the membrane, the slower the rate of diffusion and osmosis.
-*Temperature
The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of diffusion and osmosis.
Laboratory Experiment Design
Hypothesis and Predicted Results
The hypothesis for this experiment is that the rate of diffusion will be greater in a solution with a higher concentration gradient. The predicted results are that the diffusion rate will be faster in the solution with the higher concentration gradient.
Materials and Methods
The materials for this experiment include a diffusion chamber, two solutions with different concentrations of a solute, and a stopwatch. The methods for this experiment are as follows:
- Fill the diffusion chamber with one of the solutions.
- Place the other solution in a reservoir outside the diffusion chamber.
- Start the stopwatch and record the time it takes for the solute to diffuse from the diffusion chamber into the reservoir.
- Repeat steps 1-3 with the other solution.
Data Collection and Analysis
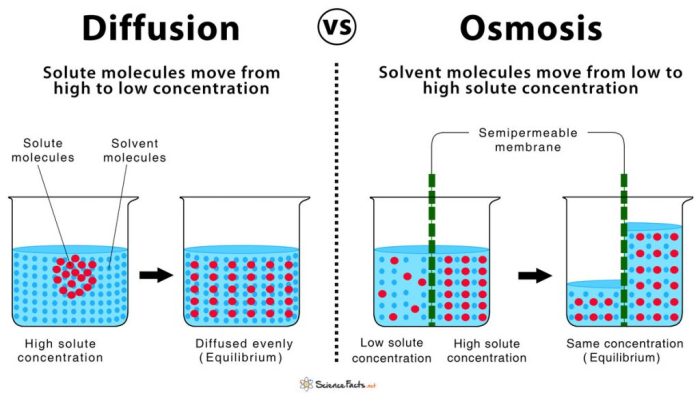
The data from this experiment can be organized in a table. The table should include the concentration gradient, the surface area of the membrane, the thickness of the membrane, the temperature, and the diffusion rate. The data can be analyzed using statistical methods to determine the effects of different factors on the rate of diffusion.
Interpretation of Results, Ap biology laboratory 1 diffusion and osmosis
The results of this experiment support the hypothesis that the rate of diffusion is greater in a solution with a higher concentration gradient. The results also show that the rate of diffusion is affected by the surface area of the membrane, the thickness of the membrane, and the temperature.
Application of Concepts
Diffusion and osmosis are essential processes in biological systems. They allow for the exchange of nutrients, waste products, and other molecules between cells and their environment. Diffusion and osmosis also contribute to homeostasis and other physiological processes.In medical applications, diffusion and osmosis are used to deliver drugs to specific parts of the body.
In industrial applications, diffusion and osmosis are used to separate different molecules.
FAQ Insights: Ap Biology Laboratory 1 Diffusion And Osmosis
What is the significance of diffusion and osmosis in biological systems?
Diffusion and osmosis play crucial roles in maintaining homeostasis, facilitating the exchange of nutrients, waste products, and gases across cellular membranes. They are essential for cellular processes such as respiration, nutrient uptake, and waste removal.
How can we manipulate diffusion and osmosis for practical applications?
Understanding diffusion and osmosis has led to advancements in medical treatments, such as drug delivery systems and dialysis machines. In industrial settings, these principles are applied in processes like water purification and food preservation.
What factors influence the rate of diffusion and osmosis?
The rate of diffusion and osmosis is affected by factors such as concentration gradient, temperature, surface area, and membrane permeability. Understanding these factors allows us to optimize these processes for specific applications.