Observation of mitosis in a plant cell – The observation of mitosis in plant cells unveils the intricate dance of genetic material during cell division, providing fundamental insights into the growth and development of plants. This detailed exploration delves into the techniques, stages, and analysis of mitosis, offering a comprehensive understanding of this crucial biological process.
Preparation of Plant Material
Observing mitosis in plant cells requires suitable plant materials that exhibit active cell division. Ideal choices include:
- Onion root tips
- Pea root tips
- Tomato root tips
- Bean root tips
To prepare the plant material:
- Select fresh and actively growing root tips.
- Cut off approximately 1 cm of the root tip.
- Place the root tips in a petri dish containing distilled water.
- Incubate the root tips for 18-24 hours at room temperature.
Fresh and actively growing tissues are essential because they contain a higher number of dividing cells, increasing the chances of observing mitosis.
Staining Techniques
Staining techniques are crucial in mitosis observation as they enhance the visibility and contrast of chromosomes.
Common staining methods include:
- Aceto-orcein staining:A simple and effective method that uses a mixture of acetic acid and orcein stain. It stains chromosomes dark purple.
- Feulgen staining:A more specific method that selectively stains DNA. It produces a red-violet color.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
| Staining Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Aceto-orcein | Simple and inexpensive | Can be messy and may overstain |
| Feulgen | Specific for DNA | More complex and expensive |
Microscopy and Observation
Mitosis observation requires a compound microscope with a magnification of 400x or higher. Optimal illumination is achieved using a bright-field condenser.
To locate and identify mitotic cells:
- Scan the slide under low magnification to identify areas with high cell density.
- Switch to high magnification and focus on individual cells.
- Look for cells with condensed and visible chromosomes.
- Identify the different stages of mitosis based on the chromosome arrangement.
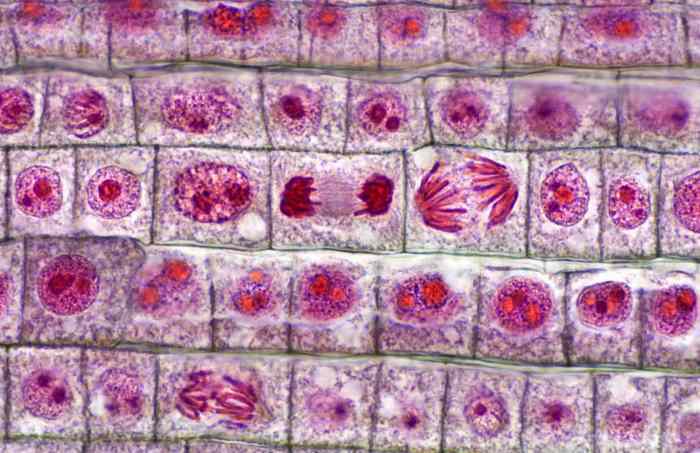
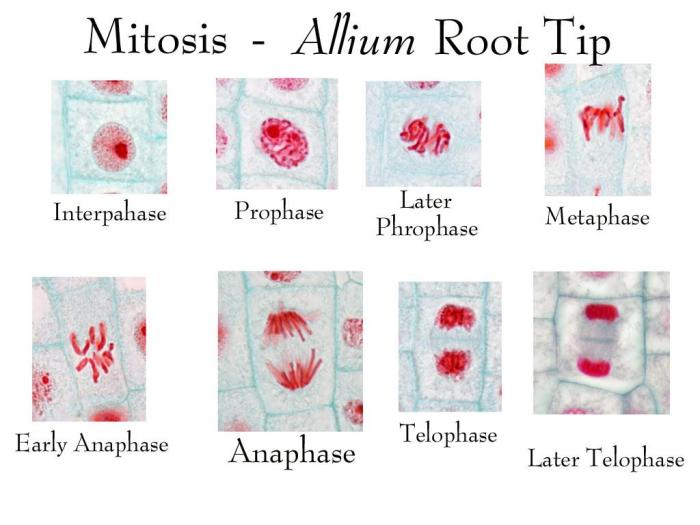
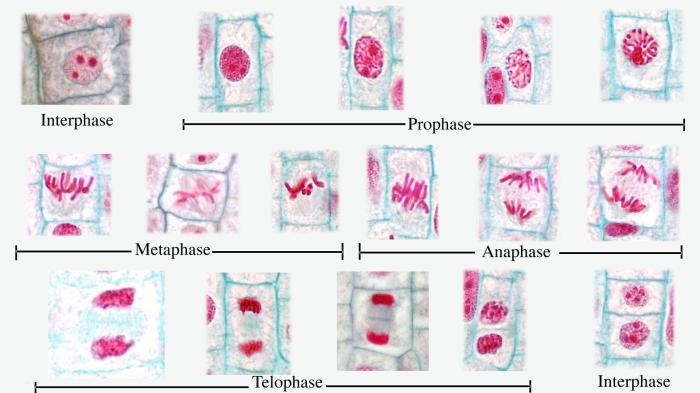
Stages of Mitosis
Mitosis consists of four distinct stages:
- Prophase:Chromosomes condense and become visible. The nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase:Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate.
- Anaphase:Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase:Two daughter nuclei form, and the chromosomes decondense. The nuclear envelope reforms.
The duration of each stage varies depending on the cell type and environmental conditions.
Data Collection and Analysis
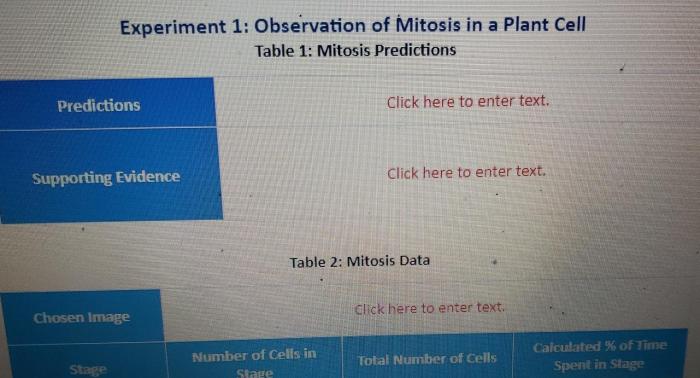
Recording observations and data is essential for mitosis analysis. Common data collected include:
- Cell counts
- Mitotic index (percentage of cells in mitosis)
- Chromosome behavior (e.g., chromosome breaks, lagging chromosomes)
Statistical methods, such as chi-square tests and ANOVA, can be used to analyze mitosis data and determine the significance of differences between groups.
Popular Questions: Observation Of Mitosis In A Plant Cell
What are the key stages of mitosis?
The key stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, each characterized by distinct chromosomal arrangements and spindle fiber dynamics.
How is staining used in observing mitosis?
Staining techniques, such as aceto-orcein and Feulgen staining, enhance the visibility of chromosomes, allowing for clear identification of mitotic stages.
What type of microscope is used for observing mitosis?
A compound light microscope with appropriate magnification and illumination settings is typically used for observing mitosis in plant cells.