FM systems are used in conjunction with hearing aids to amplify sound and improve speech clarity, particularly in challenging listening environments. These systems consist of a transmitter and receiver that wirelessly transmit sound directly to the hearing aid, bypassing background noise and reverberation.
This guide explores the compatibility, types, applications, technical considerations, installation, maintenance, user experience, and future trends of FM systems, providing a comprehensive understanding of their role in enhancing hearing aid performance.
FM Systems and Hearing Aids: Compatibility and Integration
FM systems are assistive listening devices designed to work in conjunction with hearing aids to improve sound quality and reduce listening effort for individuals with hearing loss. They consist of a transmitter, which is typically worn by the speaker, and a receiver, which is worn by the listener.
The transmitter converts sound into a radio signal, which is then transmitted to the receiver, where it is converted back into sound and delivered directly to the listener’s hearing aid.FM systems are compatible with a wide range of hearing aids, including analog, digital, and programmable hearing aids.
The type of FM system required will depend on the specific hearing aid being used. Some FM systems are designed to work with specific hearing aid models, while others are compatible with a wider range of hearing aids.
Benefits of Using FM Systems with Hearing Aids, Fm systems are used in conjunction with hearing aids to
FM systems offer a number of benefits for individuals with hearing loss, including:
- Improved sound quality: FM systems can significantly improve the sound quality of speech and other sounds by reducing background noise and reverberation.
- Reduced listening effort: FM systems can reduce the amount of effort required to listen, which can lead to less fatigue and improved comprehension.
- Increased signal-to-noise ratio: FM systems can increase the signal-to-noise ratio, making it easier to hear speech in noisy environments.
- Improved localization: FM systems can help individuals with hearing loss to better localize sound, making it easier to identify the direction from which sound is coming.
Types of FM Systems
There are a variety of FM systems available on the market, each with its own unique features and benefits. FM systems can be classified based on a number of factors, including:
- Range: FM systems can have a range of up to 100 meters, making them suitable for use in a variety of settings.
- Signal strength: FM systems can have different signal strengths, which can affect the range and reliability of the system.
- Compatibility: FM systems can be compatible with a variety of hearing aids, including analog, digital, and programmable hearing aids.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of FM Systems
The different types of FM systems have their own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common types of FM systems include:
- Personal FM systems: Personal FM systems are designed for use by a single individual. They are typically small and lightweight, making them easy to wear and transport.
- Group FM systems: Group FM systems are designed for use by multiple individuals. They are typically more powerful than personal FM systems and can cover a larger area.
- Classroom FM systems: Classroom FM systems are designed for use in classrooms. They typically include a microphone for the teacher and a receiver for each student.
Applications of FM Systems

FM systems are used in a variety of settings, including:
- Classrooms: FM systems can be used in classrooms to improve the listening experience for students with hearing loss. They can help students to hear the teacher’s voice more clearly and reduce the amount of background noise.
- Workplaces: FM systems can be used in workplaces to improve the listening experience for employees with hearing loss. They can help employees to hear their colleagues more clearly and reduce the amount of background noise.
- Social gatherings: FM systems can be used in social gatherings to improve the listening experience for individuals with hearing loss. They can help individuals to hear their friends and family more clearly and reduce the amount of background noise.
Technical Considerations
When selecting an FM system, it is important to consider a number of technical factors, including:
- Frequency range: FM systems operate on a specific frequency range. It is important to choose a system that operates on a frequency range that is compatible with the hearing aid being used.
- Signal strength: The signal strength of an FM system can affect the range and reliability of the system. It is important to choose a system with a signal strength that is appropriate for the intended use.
- Transmission protocols: FM systems use different transmission protocols to transmit sound. It is important to choose a system that uses a transmission protocol that is compatible with the hearing aid being used.
Installation and Maintenance
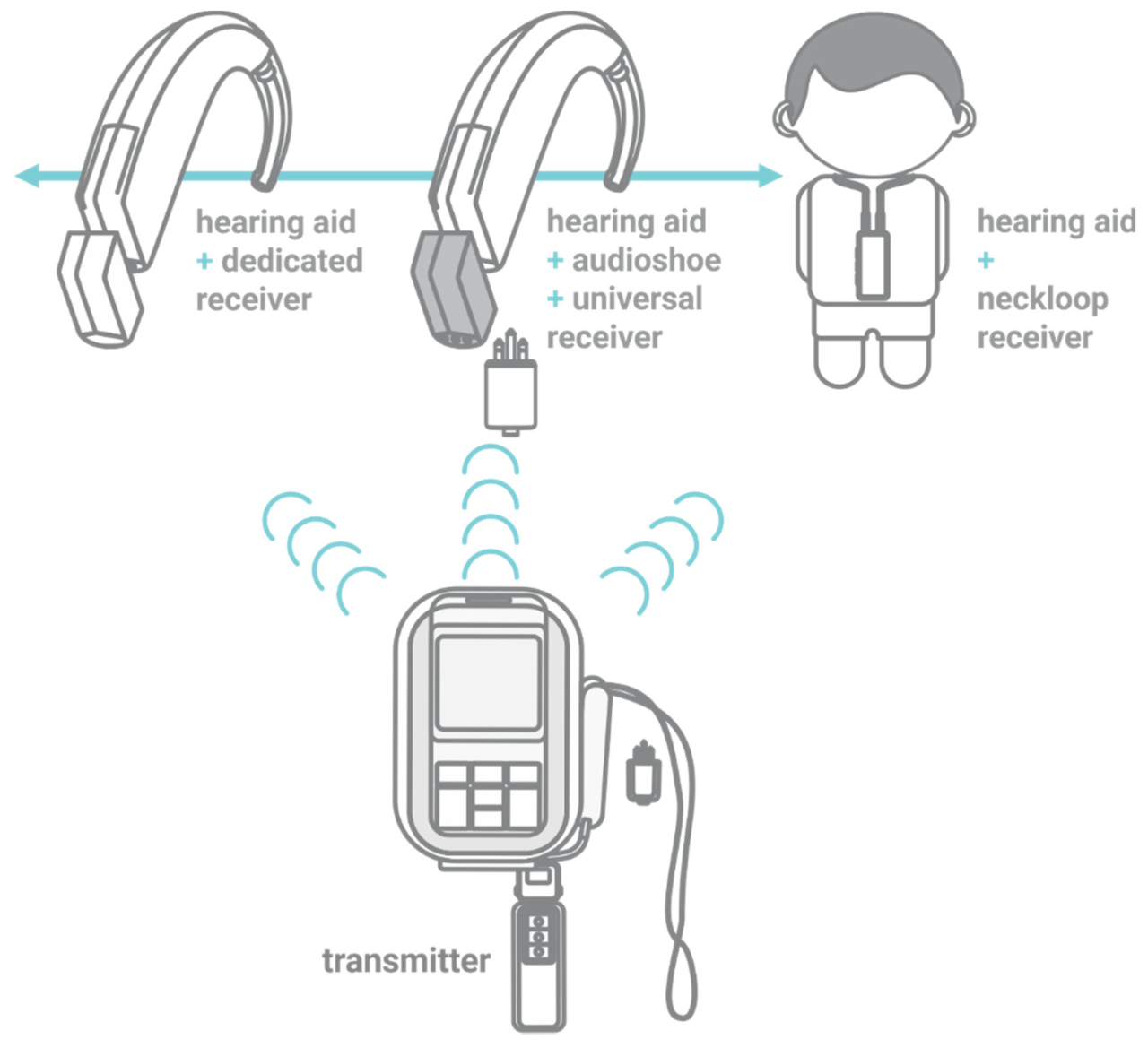
FM systems are relatively easy to install and maintain. The following steps can be followed to install an FM system:
- Choose a location for the transmitter. The transmitter should be placed in a central location so that it can reach all of the receivers.
- Connect the transmitter to the audio source. The audio source can be a microphone, a sound system, or another audio device.
- Turn on the transmitter and the receivers. The receivers should be tuned to the same frequency as the transmitter.
- Adjust the volume on the receivers to a comfortable level.
FM systems require minimal maintenance. The following steps can be followed to maintain an FM system:
- Keep the transmitter and receivers clean. The transmitter and receivers should be cleaned with a soft cloth and mild detergent.
- Replace the batteries in the transmitter and receivers as needed. The batteries should be replaced when the system starts to lose power.
- Check the connections between the transmitter and the audio source. The connections should be checked to ensure that they are secure.
User Experience and Satisfaction
FM systems can significantly improve the listening experience for individuals with hearing loss. However, it is important to note that FM systems are not a cure for hearing loss. They can only help to improve the sound quality and reduce the amount of listening effort required.The
user experience and satisfaction with FM systems can vary depending on a number of factors, including:
- The type of hearing loss: FM systems can be more beneficial for individuals with certain types of hearing loss than others.
- The environment: FM systems can be more effective in some environments than others.
- The individual’s expectations: It is important to have realistic expectations about what FM systems can do.
Future Developments and Trends
![]()
FM systems are constantly being developed and improved. Some of the latest trends in FM systems include:
- Digital FM systems: Digital FM systems offer a number of advantages over analog FM systems, including improved sound quality and reduced interference.
- Bluetooth FM systems: Bluetooth FM systems allow users to connect their hearing aids to FM systems wirelessly.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): AI is being used to develop FM systems that can automatically adjust to the user’s environment.
Top FAQs: Fm Systems Are Used In Conjunction With Hearing Aids To
What are the benefits of using FM systems with hearing aids?
FM systems improve sound quality, reduce listening effort, and enhance speech clarity in noisy environments.
What types of hearing aids are compatible with FM systems?
Most modern hearing aids are compatible with FM systems, including behind-the-ear (BTE), in-the-ear (ITE), and in-the-canal (ITC) models.
How do I install and configure an FM system?
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Typically, the transmitter is placed near the sound source, while the receiver is attached to the hearing aid.